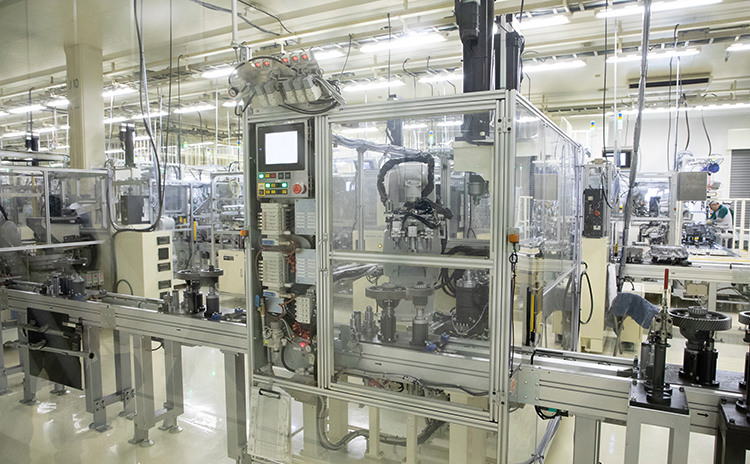
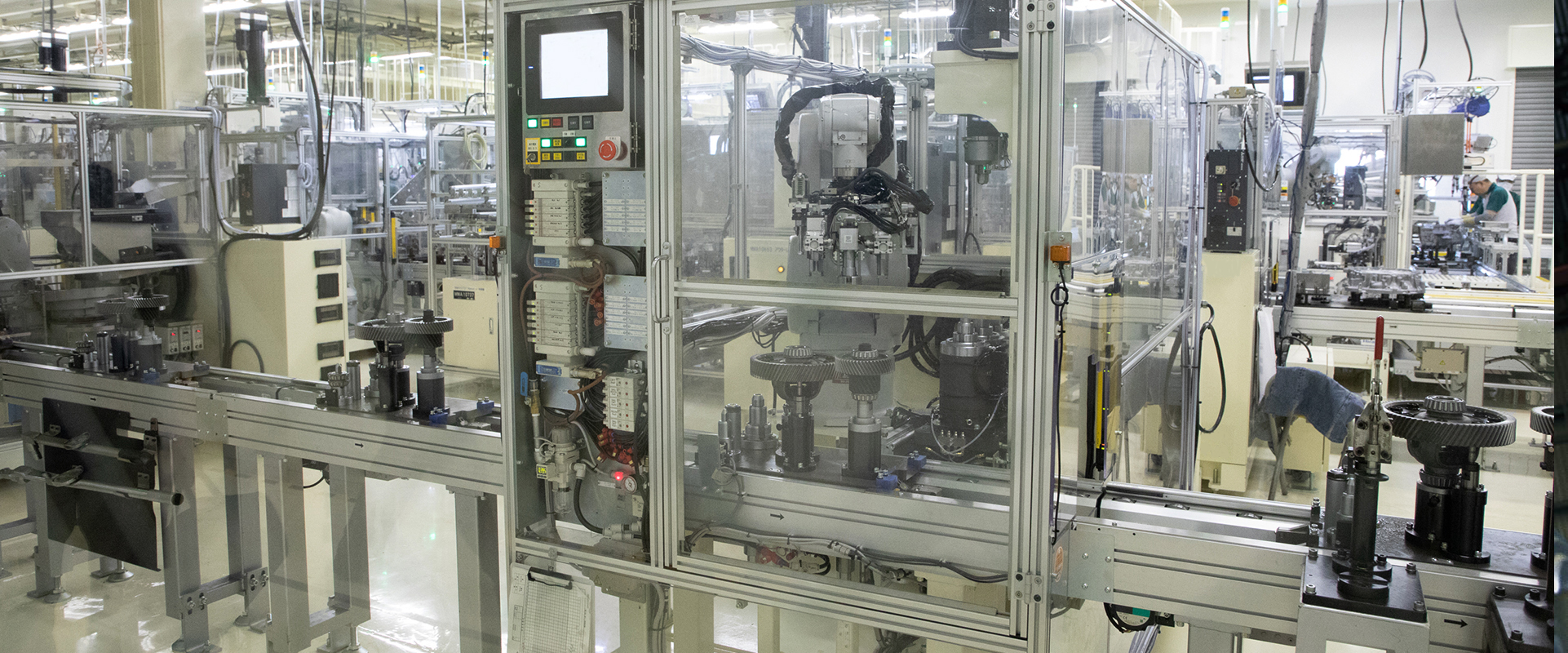
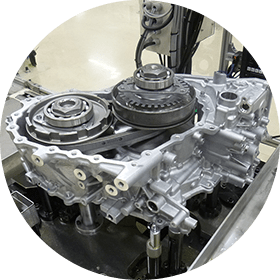
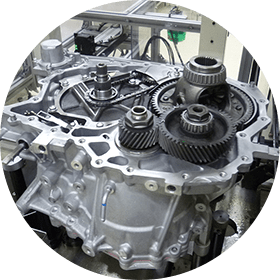
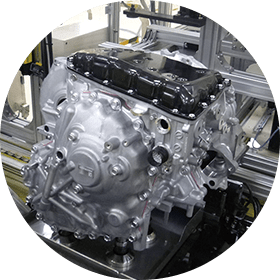
Forging
The process of "adding force to change the shape of objects" is referred to as plasticity forming. Among plasticity forming methods, "forging" in which parts are made by pressing materials into a mold using strong force, possesses the attribute of producing highly durable parts.

Steel material
Cylindrical steel pieces

Cutting
Material is cut to length

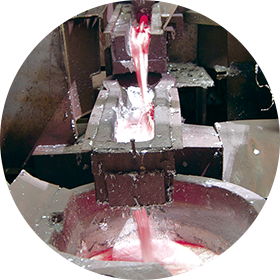
Heating
Heating prior to forging

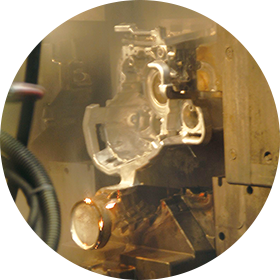
Forging
Stamping to shape
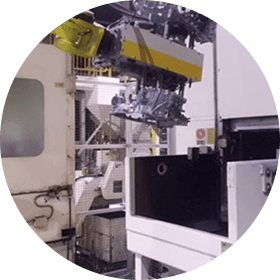
Magnetic Particle Testing
Inspection for scratches, cracks

Exterior check